Cenozoic Era – Time for Ancient Life
The Cenozoic Era, named after the Greek for ‘New Life’, is split into three geological periods.
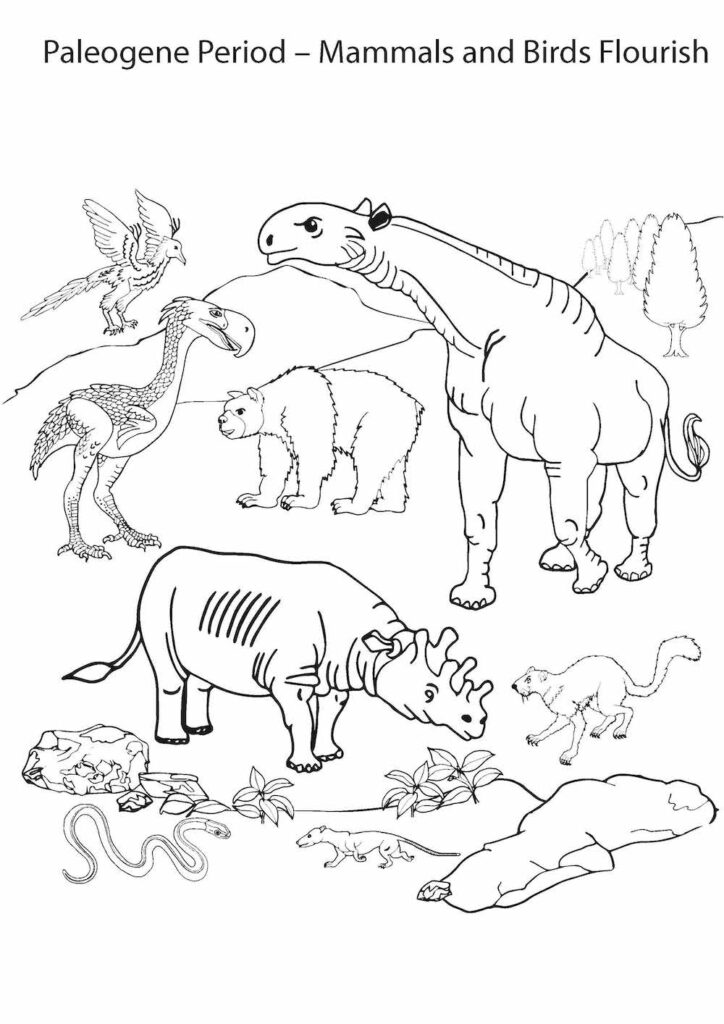
Cenozoic Era 1: Paleogene Period – Mammals and Birds Flourish
Key Events
- Continents drift towards their current positions.
- With the dinosaurs extinct, mammals and birds become dominant.
- Mammals evolve, grow larger and diversify:
- Species including the first rhinos, horses, camels, bears, dogs and cats occupy the land.
- The first primates (relatives of humans) take to the trees.
- Cetaceans (which include whales and dolphins) evolve in the seas.
- Plants adapt to the cool conditions, with the first grasses appearing.

Facts, Debates & Trivia
- The Paleogene name is derived from the Greek for ‘Old Birth’.
- The success of mammals is attributed to their development of the placenta, which enablesthem to protect and nourish babies in the womb and give birth to relatively mature infants.
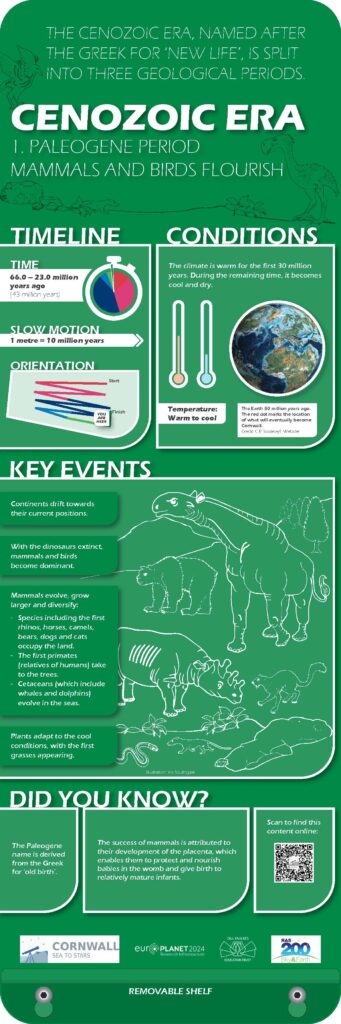
Conditions
- The climate is warm for the first 30 millions years.
- During the remaining time, it becomes cool and dry.
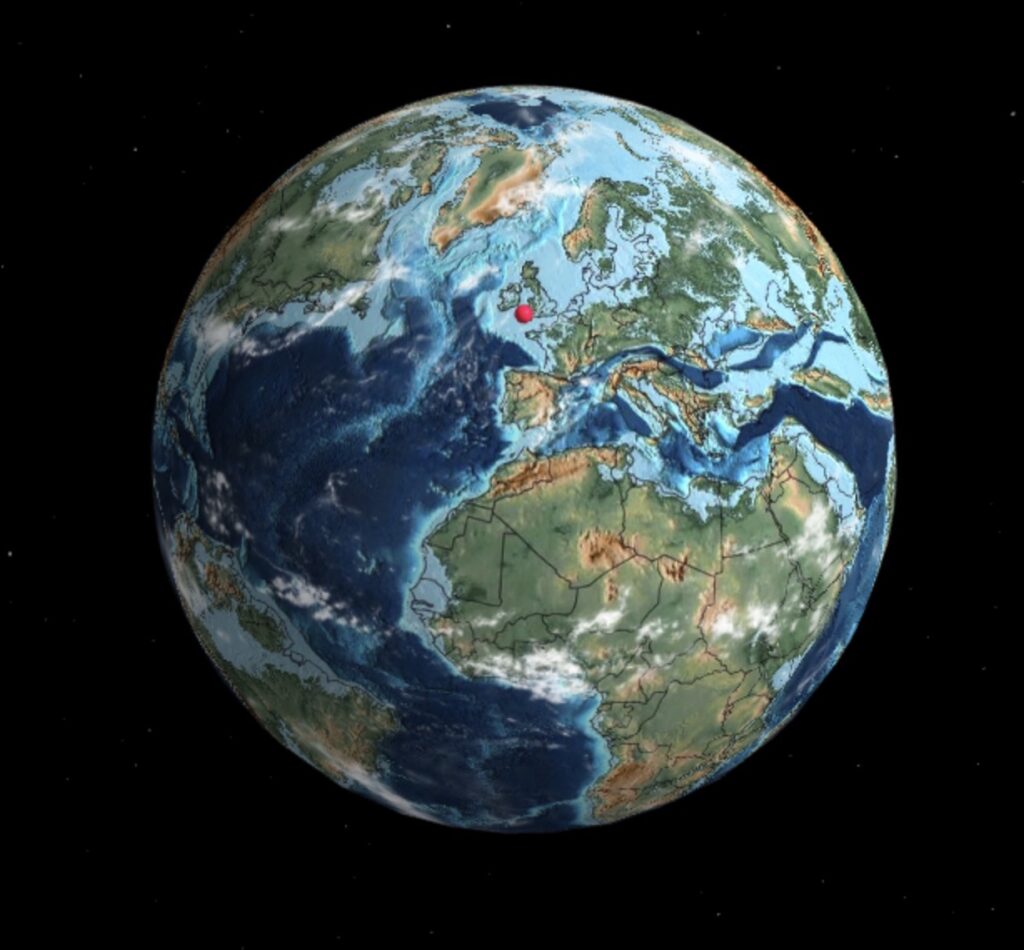
Timeline
201.3 – 145.0 million years ago
(56.3 million years)

Where have you reached on the trail?


